St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
Peijun Ma Lab
Investigating the impact of bacterial heterogeneity on antibiotic resistance and persistence using bacterial single-cell transcriptomics
About the Peijun Ma lab
Antibiotics are a proven treatment method in bacterial infections. But bacteria’s ability to form resistance to antibiotics and persist has become an increasing point of concern, especially in people receiving treatment and who may become immunocompromised. Emergence of antibiotic resistance can directly lead to treatment failure, posing a threat to overall outcomes and human health. Our research investigates the diverse nature of bacteria populations to better understand and characterize how this diversity arises and how resistance can form as a result.

Our research summary
A limiting factor in current efforts to combat antibiotic resistance and persistence is the predominant characterization of bacteria as whole populations. This homogenization has restricted the proper characterization of bacterial populations as diverse and heterogeneous.
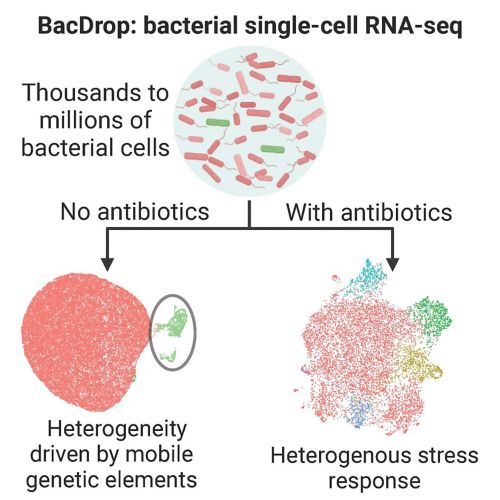
With the knowledge that resistant and persistent clones typically arise from single-cell events, breaking away from a homogenous view of bacteria populations and investigating the mechanisms behind their heterogeneity will help us understand how resistance and persistence can be mitigated. To do this, we will apply innovative bacterial single-cell transcriptomics to characterize bacterial drug-induced heterogeneity at the single-cell level.
Part of understanding how best to mitigate resistance and persistence is to understand how bacteria behaves in the host microenvironment.
To achieve this, we characterize the microbiome using bacterial single-cell transcriptomics to understand the evolution of resistance and persistence in the context of the host microenvironment, particularly in patients with recurrent bacterial infections.

Our work will provide novel insight into bacterial heterogeneity and identify therapeutic targets to treat bacterial infections associated with antibiotic resistance and persistence. By contributing research that helps characterize the heterogeneity of bacterial populations and examining the origins of resistance and persistence at the single-cell level, we hope to advance that will allow successful treatment for pediatric catastrophic disease.
Publications
Contact us
Peijun Ma, PhD
Assistant Member, St. Jude Faculty
Department of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences
MS 313, Room I5106B
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital
Memphis, TN, 38105-3678 USA GET DIRECTIONS