St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
Fibcd1 to treat or prevent muscle wasting (SJ-20-0008)
St. Jude Reference #SJ-20-0008
Description
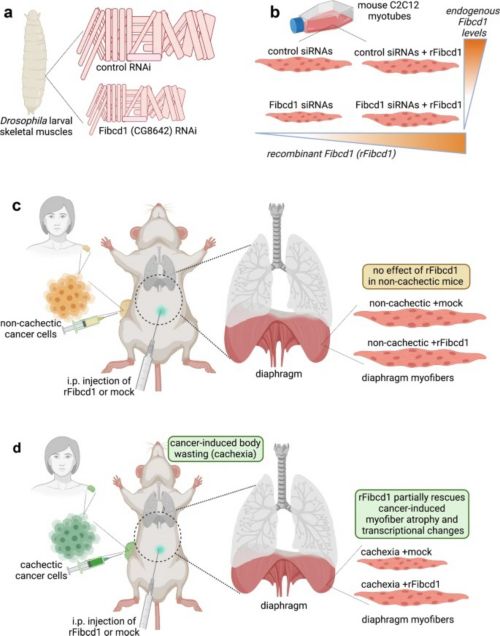
While there are many physical therapies and exercises to help rebuild muscle, there is no clinical therapeutic for prevention of skeletal muscle wasting. Decline in skeletal muscle cell size (myofiber atrophy) is a key feature of cancer-induced wasting (cachexia); in particular, atrophy of the diaphragm, the major muscle responsible for breathing, is an important determinant of cancer-associated mortality. Researchers at St. Jude searching for solutions to this unmet need found that a recombinant protein Fibcd1 (recombinant Fibrinogen C Domain Containing 1) variant rescues the decrease in muscle cell size (myofiber atrophy) that is a feature of many human disease conditions, such as cancer, aging, diabetes, neurological disorders, infections, bed rest or cast immobilized limb, corticosteroid or other drug use, and others; and a worsening factor for prognosis.
Their proposed invention is a systemic or local injection of human rFibcd1 used to rescue and/or prevent the loss of muscle mass (muscle wasting) that occurs due to myofiber atrophy with many disease conditions.
Keywords
Muscle wasting due to cancer, aging, diabetes, neurological disorders, infections, bed ridden
Granted Patents or Published Applications
Pending International Application published as WO 2021/173616
Related Scientific References
Graca, F.A., Rai, M., Hunt, L.C. et al. The myokine Fibcd1 is an endogenous determinant of myofiber size and mitigates cancer-induced myofiber atrophy. Nat Commun 13, 2370 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30120-1
Licensing Opportunities
We are seeking partners to develop systemic rFibcd1 injection, or localized injection to preserve the mass and function of key muscles (such as the diaphragm, which is needed for breathing), to promote the maintenance of the mass of muscles in a cast-immobilized limb, or etc. Contact: chad.riggs@stjude.org
Contact the Office of Technology Licensing (Phone: 901-595-2342, Fax: 901-595-3148) for more information.