St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
Genetics of sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an inherited red blood cell disorder stemming from abnormal hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is an oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells that, early in development, consists of two α-like globin peptides and two γ-like globin peptides (fetal hemoglobin). After birth, the composition of hemoglobin changes to two α-like globin peptides and two β-like globin peptides (adult hemoglobin). This distinct structural alteration happens because of the transition from the expression of two paralogous fetal γ-like globin genes, HBG1/HBG2, to the expression of the HBB gene, which encodes the β-globin subunit of adult hemoglobin.
As we age, fetal hemoglobin is replaced by adult hemoglobin and, therefore, individuals harboring autosomal recessive mutations in HBB begin to experience symptoms. At low oxygen concentrations, mutant adult-type sickle hemoglobin forms polymers resulting in sickle shaped, sticky red blood cells. Clinically, this translates to anemia, organ damage and pain crises.
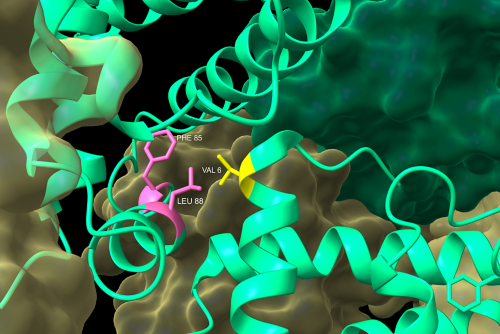
Close-up of the molecular interface of the β subunits (green) of two sickle cell anemia hemoglobin S tetramers. When the β subunit of hemoglobin harbors a Glu6Val transversion mutation (yellow), a hydrophobic pocket is created on the surface of the protein. This allows for the interaction of one tetramer’s valine to interact with the hydrophobic side chains of the neighboring tetramer’s surface-exposed phenylalanine and leucine (pink). This dimerization event is the beginning of the formation of a chain of polymerized tetramers that, ultimately, misshapes red blood cells causing the characteristic sickle shape. Rendering made with ChimeraX (PDB: 2HBS).
How treatments are born
St. Jude researchers have played integral roles in advancing our understanding of SCD, and therapies born from basic research have been successfully translated into clinical therapies for children with SCD. In fact, the first research grant St. Jude received was dedicated to studying SCD and to this day, St. Jude continues its dedication to SCD treatments and cures. The institution has one of the largest SCD treatment programs in the country, caring for almost 1,000 children with SCD and even offering assistance with transition care.
Leveraging their understanding of the science behind the blood disorder, St. Jude researchers surmised that the effects of SCD could be ameliorated by modulating the amount of fetal hemoglobin present in red blood cells. Some of the most recent advances in the treatment of SCD have centered on this concept.
Hydroxyurea
St. Jude researchers played a pivotal role in identifying hydroxyurea as a safe and effective treatment for sickle cell anemia in very young children. Hydroxyurea augments fetal hemoglobin levels and inhibits the polymerization of sickled adult hemoglobin. St. Jude-led studies showed that this drug lessened acute pain, lowered the number of blood transfusions and hospitalization rates for infants and toddlers. Research pertaining to hydroxyurea, including novel ways to increase adherence, is ongoing as it continues to be a first line of treatment for many with SCD.
Regulation of fetal hemoglobin
Modulating fetal hemoglobin requires an understanding of the basic science driving γ-globin gene expression. Researchers have made important discoveries that tease apart the regulation of fetal hemoglobin. Two activator sequences and repressor sequences were identified, which aid in modulating the γ-to-β-globin gene switch, and researchers have also discovered that hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF1) promotes expression of γ-globin under low-oxygen conditions. Studies like these provide a clearer understanding of the regulation of fetal hemoglobin and open the door for the development of new therapeutic targets.
Experiments aimed at understanding the regulatory circuitry controlling fetal hemoglobin expression are ongoing and will most certainly lay the foundation for the next generation of clinical treatments.
Genome editing: The next generation of SCD treatments
In the 1980s, a St. Jude patient was undergoing a bone marrow transplant for leukemia. This treatment also eliminated her sickle cell anemia. The case study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, proved that bone marrow transplantations could cure SCD.
While transplantation has approximately an 85% success rate (if the donor is a relative and human leukocyte antigen-matched), this approach is limited to a select few patients—less than 20%—due to the potential for complications, thus underscoring the need for alternative treatment options.
With the advent of genome editing, St. Jude researchers have developed and optimized gene editing strategies for SCD. Researchers have set their sights on applying genome editing to induce fetal hemoglobin in patients.
St. Jude established the St. Jude Collaborative Research Consortium for Sickle Cell Disease (CRC-SCD) aimed at teasing apart the molecular mechanisms enabling the γ-to-β-globin gene switch and how to precisely control this switch. The CRC-SCD has focused on how to utilize gene therapy strategies such as CRISPR-Cas9, base editing and prime editing to treat SCD.
CRISPR-Cas9
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing of hematopoietic stem cells was one of the first genome editing strategies employed for SCD. St. Jude researchers showed that CRISPR-Cas9 technology could successfully mutate a short nucleotide sequence in the promoters of HBG1 and HBG2, leading to an increase in fetal hemoglobin. This finding identified attractive DNA targets for SCD and other β-hemoglobinopathies and has subsequently shown to be effective in clinical studies.
Base editing
St. Jude scientists are also on the cutting edge of adapting novel genome strategies to treat SCD. Base editors combine CRISPR-Cas9 technology with a nucleoside deaminase, resulting in specific transition and transversion mutations in a desired target region. Base editors have shown great promise in preclinical studies and have recently been used to create a TAL1 transcription factor binding site to induce fetal hemoglobin. The results showed this approach was more precise than CRISPR-Cas9, consistently raised fetal hemoglobin levels and should continue to be tested in a translational capacity.
Prime editing
Furthermore, researchers have demonstrated that a newer type of genome editing, called prime editing, can efficiently replace disease-causing mutations in the adult hemoglobin gene with a healthy gene sequence. Prime editing can facilitate insertions, deletions and 12 types of point mutations. Results of a 2023 publication showed that a prime-edited correction converted up to 41% of blood stem cells from SCD patients. Considering that prior work has shown that conversion rates over 20% are likely to be therapeutically relevant, this approach stands to greatly inform the next generation of SCD treatments.
The future of SCD treatments
Researchers are focused on the development of newer, more sensitive and efficient ways to utilize genome editing technology and minimize off-target effects. Dedicated basic and translational research programs here at St. Jude will allow treatment strategies to move from simply managing symptoms to a more preventative approach, thereby circumventing multisystem organ damage that so often occurs in those with SCD.
Sickle Cell Resources

Sickle cell disease data portal
The Sickle Cell Disease Portal offers robust genomic and clinical data from cohorts of individuals with sickle cell disease. This data, offered on the St. Jude Cloud, is easily and securely available to academic researchers. Genetic modifiers strongly influence outcomes in sickle cell disease. The goal of the Sickle Cell Disease Portal is to promote global collaborative efforts to understand the genetic underpinnings of the disease and develop better therapies.

St. Jude Collaborative Research Consortium for Sickle Cell Disease (CRC-SCD)
St. Jude has established the St. Jude Research Collaboratives Program. These consortia leverage renowned scientists' and clinicians' insights and capabilities to create collaborative teams committed to tackling groundbreaking projects that accelerate scientific research to pursue cures for pediatric diseases. Learn more about how this program is advancing sickle cell research.

Read more about sickle cell disease on Progress: A Digital Magazine
- Shortening the gap between pediatric and adult care improves sickle cell outcomes
- Collaborating for care: Developing a new global standard for sickle cell disease
- St. Jude advice to young adults with sickle cell disease: Stay connected
- Gene editing holds the promise of a sickle cell cure
- Boot camp trains sickle cell disease ‘pain crises champions’ to improve patient care
- Moving mountains to improve hematological care worldwide
- Bone marrow transplantation for sickle cell disease improves myocardial fibrosis












