St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising

The Center of Excellence for Innate Immunity and Inflammation (CoE-III) uses cutting-edge and industry-leading experimental and clinical approaches to answer fundamental questions about how the innate immune system recognizes and responds to invading pathogens, homeostatic perturbations, oncogenesis, and inflammatory signaling to translate research findings into innovative strategies for therapeutic intervention. The CoE-III is led by Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti, PhD of the Department of Immunology.
Our Mission
To define the fundamental mechanisms of innate immunity and inflammation to prevent, treat, and cure inflammatory and infectious diseases and cancer.
Our Research
Innate immunity is the first line of defense against pathogens and damage within the body, and inflammation is its initial response. Genetic mutations in innate immunity underlie many infectious, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases, as well as cancers.
At the core of innate immunity and inflammation research is the investigation of pathogen- and damage-associated molecular pattern sensing mechanisms and the elucidation of downstream signaling cascades. This molecular machinery is central to preventing infectious diseases, and failure to regulate innate and inflammatory responses leads to inflammatory, autoimmune, neurodegenerative, and metabolic diseases and cancers. Therefore, innate immune pathways are central to therapeutic strategies across the disease spectrum.
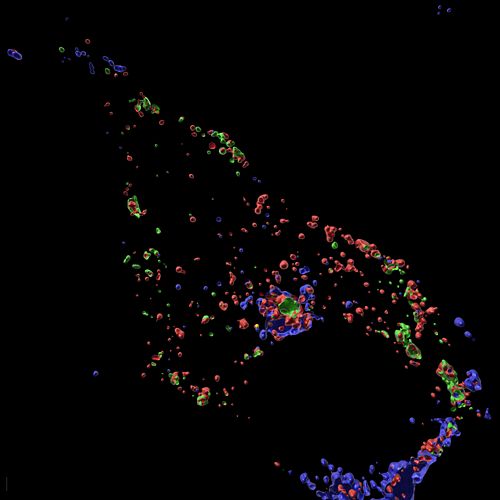
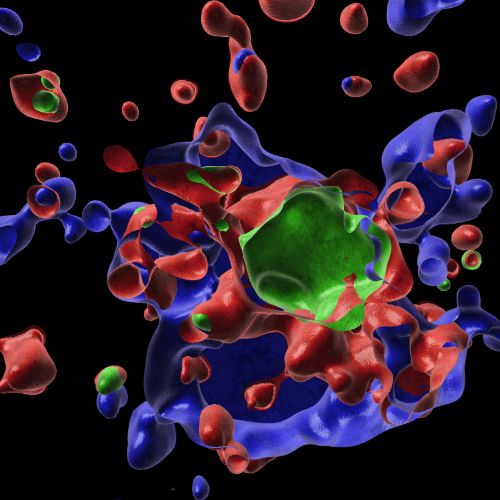
Infection with herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV1) induces innate immune activation to drive the formation of the AIM2-PANoptosome. This multi-protein complex leads to innate immune-mediated cell death, a key mechanism for host defense against this virus. These expansion microscopy images show that the AIM2-PANoptosome contains many innate immune sensing and cell death molecules, including caspase-8 (green), ASC (blue), and RIPK3 (red).
Using our advanced tools in molecular, cellular, chemical, and structural biology, genetics, and immunology, the CoE-III will perform mechanistic studies to define this biological system. Through its efforts, the Center will support and further the broader mission of St. Jude to advance cures, and means of prevention, for pediatric catastrophic diseases through research and treatment.
The CoE-III focuses on three primary research areas:
- Fundamental mechanisms of III: discovering basic biology and fundamental innate immune and cell death concepts to form a foundation for identifying therapeutic targets and developing disease treatments.
- Channeling the untapped power of III in cancer: investigating signaling cascades to identify triggers, host cell receptors, intracellular signaling molecules, and cytokines involved in innate immune-mediated processes in cancer for therapeutic benefit.
- III in neuroinflammation: investigating how the innate immune system and inflammatory signaling cascades contribute to central nervous system health and disease to improve patient outcomes.
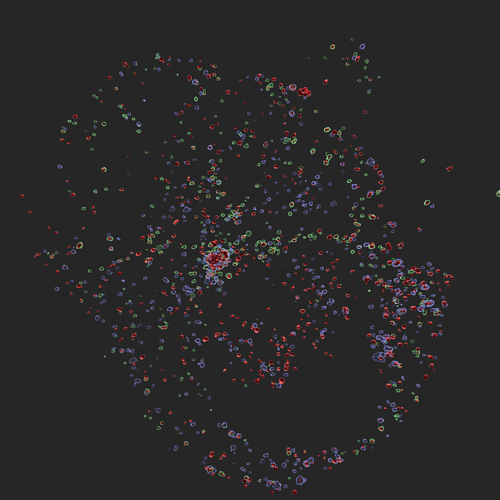
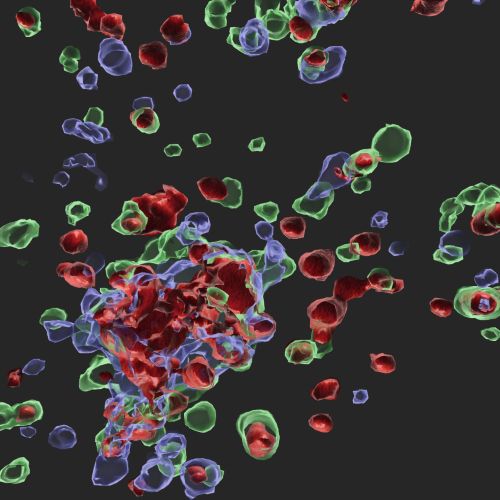
Infection with influenza A virus (IAV) induces innate immune activation to drive the formation of the ZBP1-PANoptosome. This multi-protein complex leads to innate immune-mediated cell death, a key mechanism for host defense against this virus. The ZBP1-PANoptosome contains many innate immune sensing and cell death molecules. A cell stained for the key PANoptosome molecules caspase-8 (green), ASC (blue), and RIPK3 (red) is shown here.
CoE-III Research Groups
Dr. Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti Lab
Fundamental mechanisms of III

Why St. Jude
The St. Jude Children's Research Hospital research community fosters a highly interactive environment with plentiful collaborative opportunities across our basic research and clinical departments and access to state-of-the-art High Performance Computing (HPC) facilities and outstanding Shared Resources and Core Facilities managed by highly engaged Ph.D. level scientists. The $412M Advanced Research Center, opened in 2021, doubles the campus’s research space and adds support for an additional 1,000 employees. Clinically, St. Jude is consistently ranked Top 10 in the U.S. in Pediatric Cancer and is the only NCI-designated Comprehensive Cancer Center devoted solely to children, and hosts the Pediatric Cancer Genome Project. St. Jude’s commitment to ensuring no child dies in the dawn of life extends across the disease spectrum, and basic and clinical researchers work together every day to advance this mission.